BMW Big Boxer

BMW has let some detail out of the bag about the new generation Big Boxer that will power a new cruiser range scheduled to debut in 2020 from BMW Motorrad.

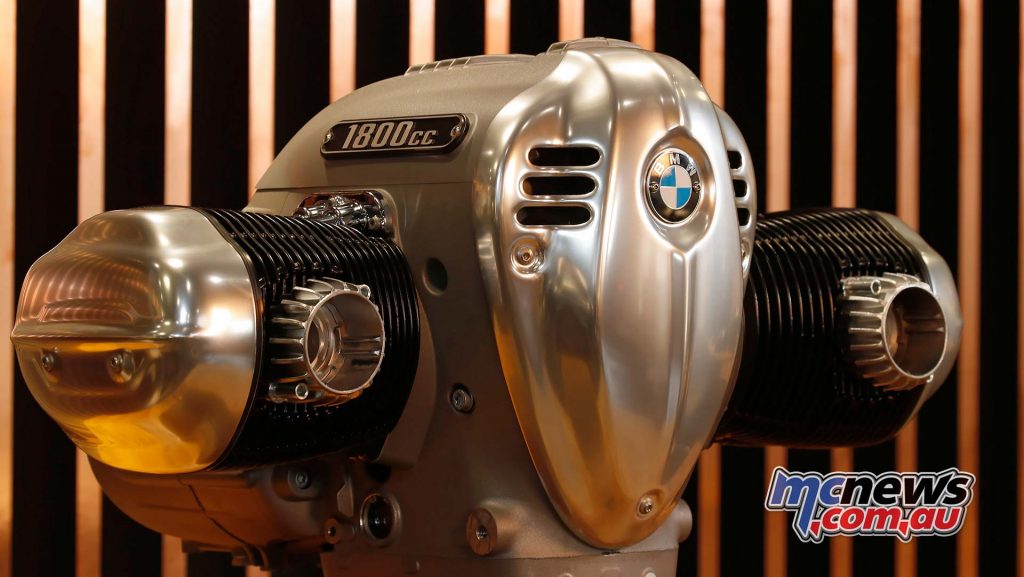
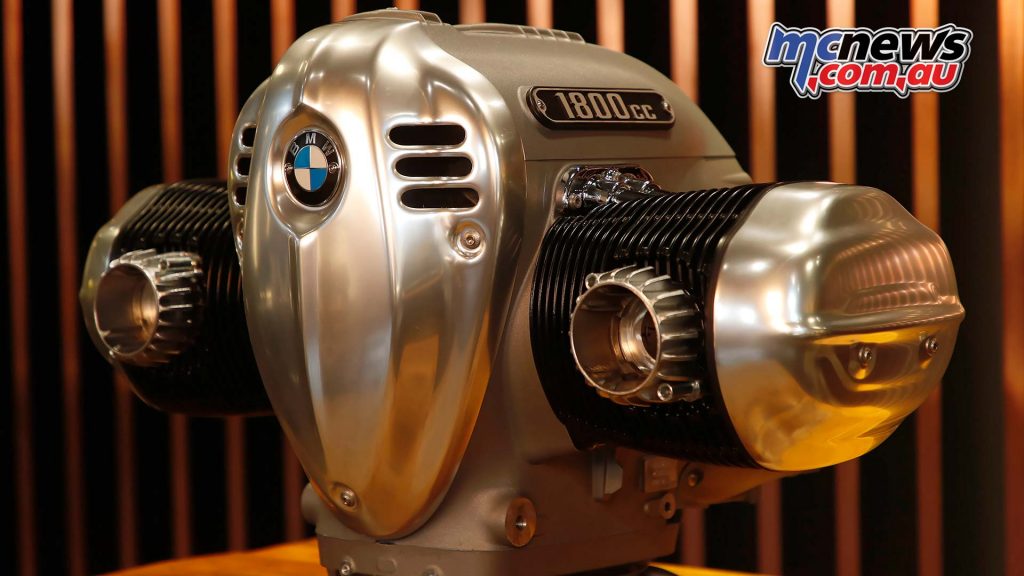
A combination of art deco design cues fuelled by nostalgia and history have driven the desing of the new 1802 cc is a beautiful showpiece that delivers 158 Nm of torque and 91 horsepower. Those numbers are pretty much line-ball with Harley-Davidson’s 114 cube Milwaukee Eight.
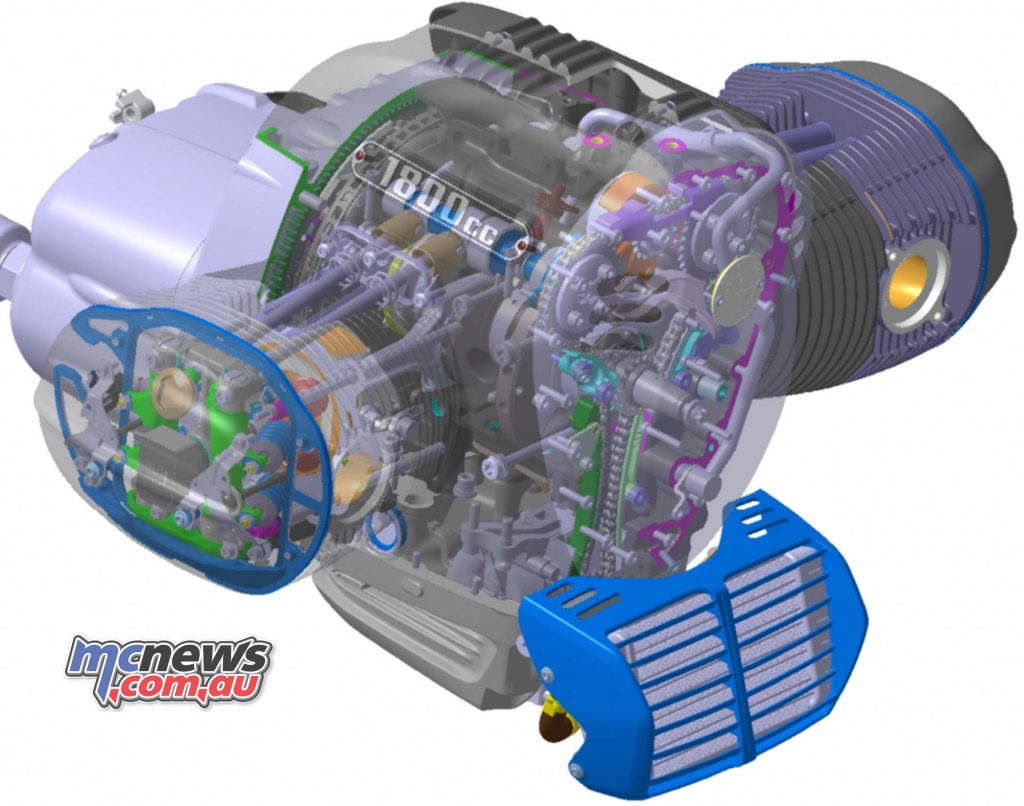
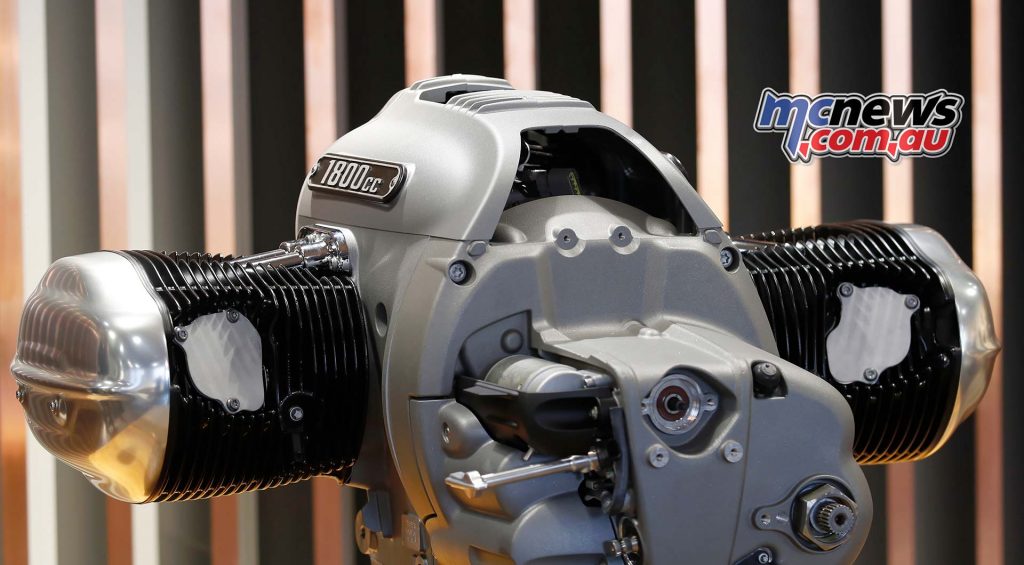
With its OHV valve drive along with a separate engine and transmission housing, the new “Big Boxer” has the same structural features that distinguished the very first BMW Motorrad boxer engine, which at that time had laterally controlled valves.
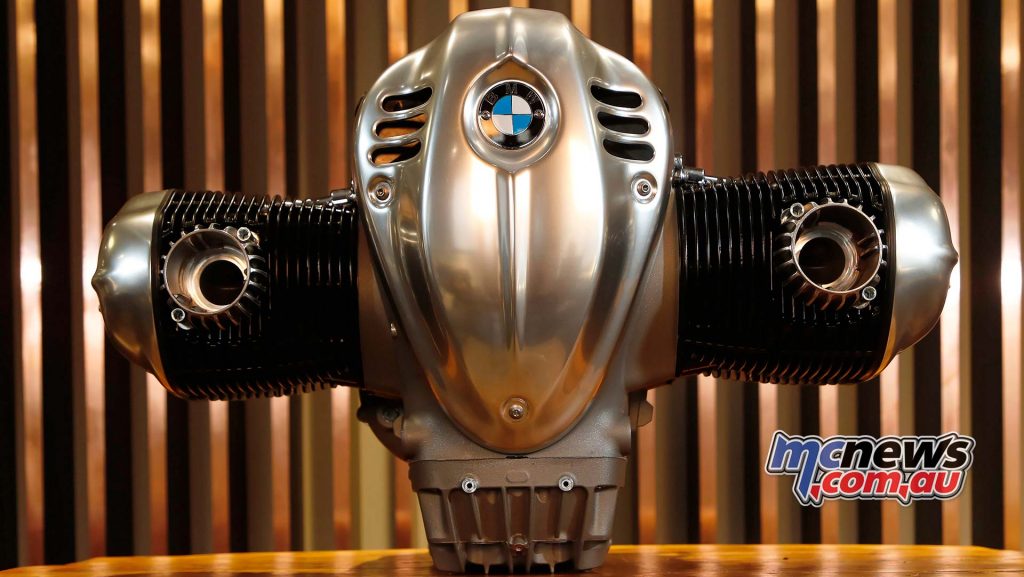
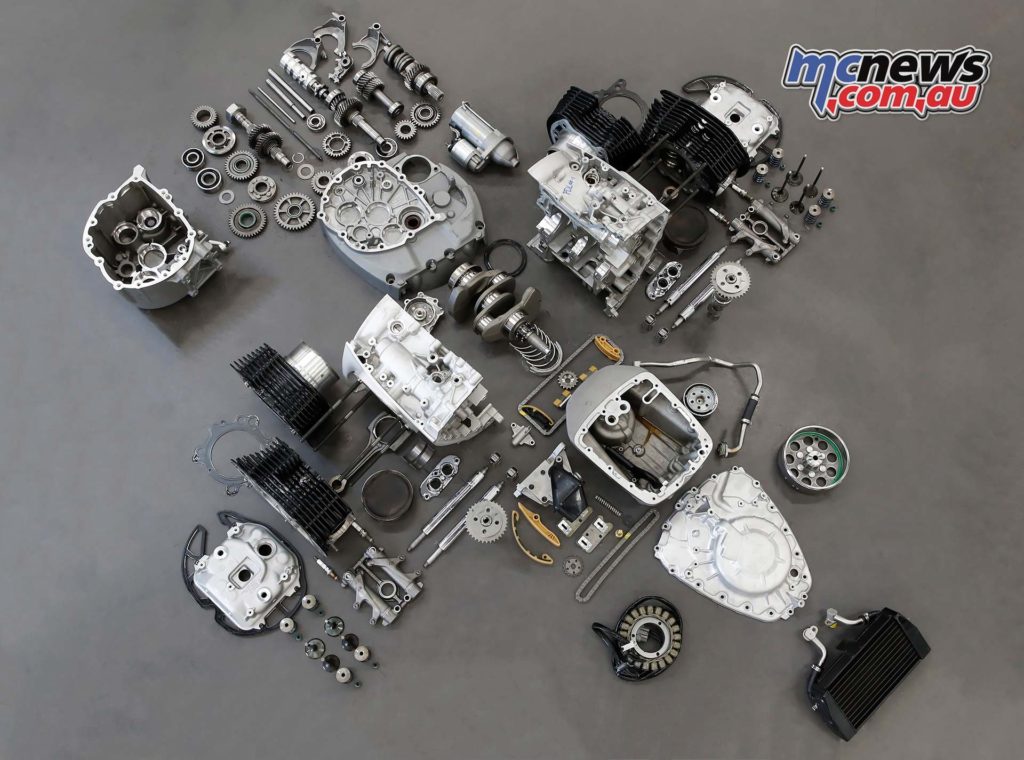
The highest-capacity twin-cylinder boxer engine ever used in motorcycle series production is a 1802 cc engine, resulting from a 107.1 mm bore and 100 mm stroke. The engine output is 67 kW (91 hp) at 4750 rpm. The maximum torque of 158 Nm is already available at 3 000 rpm. More than 150 Nm is now available from 2000 to 4000 rpm. The maximum engine speed is 5750 rpm, while the idling speed is 950 rpm.
The new “Big Boxer” is air/oil cooled, has large ribbed cylinders and cylinder heads and weighs 110.8 kg including gearbox and intake system. It has a vertically split aluminium engine housing.

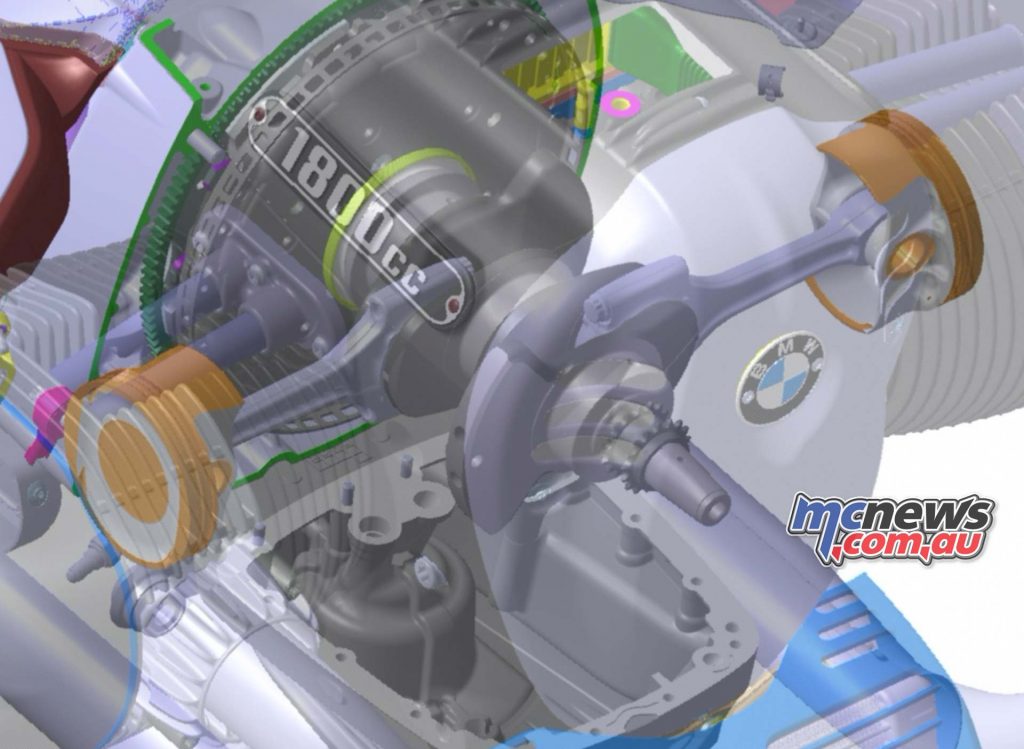
Unlike the classic air-cooled 2-valve boxer engines made by BMW Motorrad, however, the “Big Boxer” crankshaft, forged from quenched and tempered steel, has an additional main bearing at the centre, which was necessary due to the enormous cylinder volume in order to prevent undesirable bending vibrations of the crankshaft.
Like the crankshaft, the two connecting rods with I-shaft are mounted on plain bearings and are likewise forged from quenched and tempered steel. They accommodate cast aluminium pistons with two compression rings and an oil wiper ring. The running surface of the light metal cylinders is coated with NiCaSil.
Lubricating and cooling oil is supplied by a wet sump lubrication system with a two-stage oil pump via sleeve-type chain driven by the crankshaft.

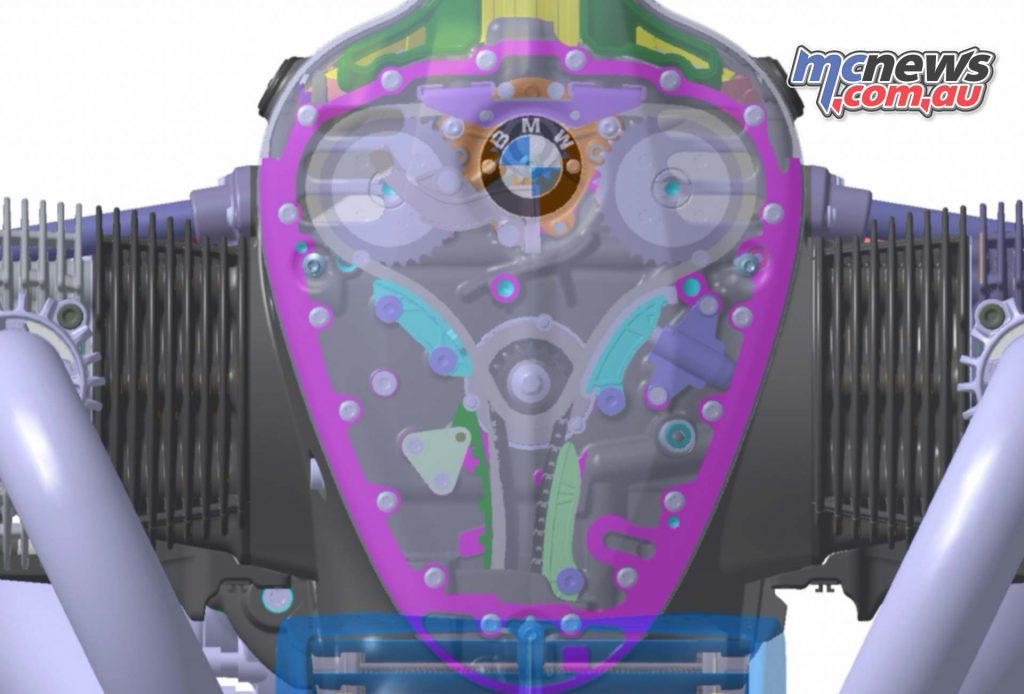
Although the new “Big Boxer” has four valves, dual ignition, a modern combustion chamber architecture, intake manifold injection and the BMS-O engine management system for the best possible torque as well as optimum consumption and emissions, it uses the classic OHV configuration for its valve drive – as was the practice pursued by BMW Motorrad over a period of some 70 years.
When developing the valve drive for the “Big Boxer”, BMW Motorrad engineers were inspired by a very special engine design in the history of BMW Motorrad – in keeping with the Heritage concept: the 2-cylinder boxer engine of the R 5/R 51 (1936 – 1941) and R 51/2 (1950 – 1951), the latter having been the first BMW motorcycle with a boxer engine after the Second World War. In contrast to other OHV designs by BMW Motorrad, this engine – highly valued by connoisseurs – has two camshafts driven by the crankshaft via a sleeve-type chain.
As in the historical role model, the two camshafts are also positioned to the left and right above the crankshaft in the “Big Boxer”. The advantage of this “twin camshaft boxer” is the shorter pushrods. This also makes for reduced moving masses, minimised deflections and lower linear expansions. A generally stiffer valve drive with improved control precision and higher speed stability is the consequence of this more elaborate construction.
In the traditional BMW Motorrad boxer design, the two pushrods actuate one pushrod per cylinder side for the intake and one for the exhaust side, guided in a sealed pushrod tube on the top of the cylinders. The two intake and exhaust valves in the cylinder head are actuated in pairs via fork toggle levers.

In contrast to today’s widespread engine technology, valve clearance compensation is not effected by means of hydraulic elements, but – as was the case in most classic air-cooled BMW two-valve boxers for decades – via one adjusting screw with one lock nut for each valve. As was formerly the case in the classic 2-valve boxers, valve clearance adjustment (0.2 – 0.3 mm) in the R18 “Big Boxer” is also achieved very quickly. The valves are made of steel, with a disc diameter of 41.2 mm on the inlet side and 35 mm on the outlet side. The valve angle is 21 degrees on the inlet side and 24 degrees on the outlet side.

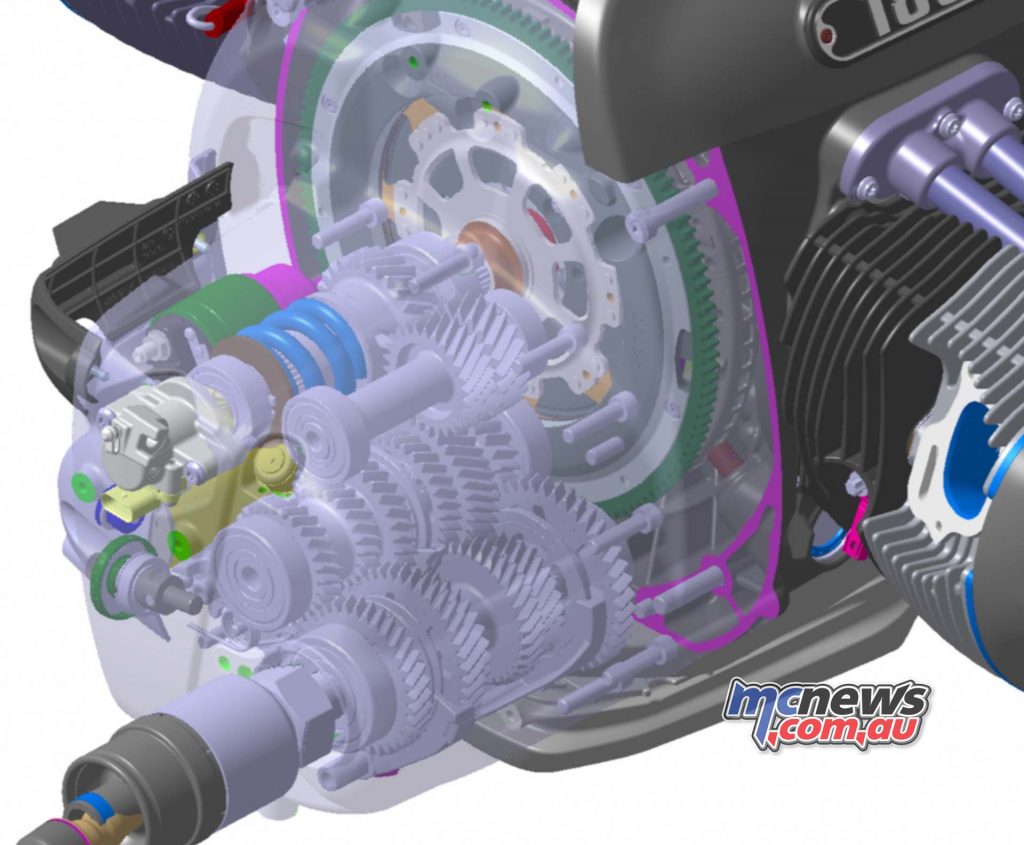
As in most BMW Motorrad boxer engines for decades (with the exception of vertical-flow, air/water-cooled boxers since 2012), a single-disc dry clutch transmits the torque generated by the engine to the transmission. For the first time it is designed as a self-reinforcing anti-hopping clutch, thereby eliminating unwanted stamping of the rear wheel caused by engine drag torque in the event of hard downshifting.
The constant mesh 6-speed transmission is located in a dual-section aluminium housing and is designed as a 4-shaft transmission with helical gear pairs. The gearbox input shaft with lug dampers drives the two gearbox shafts with the gear wheel pairs. An output shaft is provided to bridge the distance and reverse the direction of rotation. A reverse gear is available as an optional extra. This is driven by an intermediate gear and an electric motor and can be shifted manually.
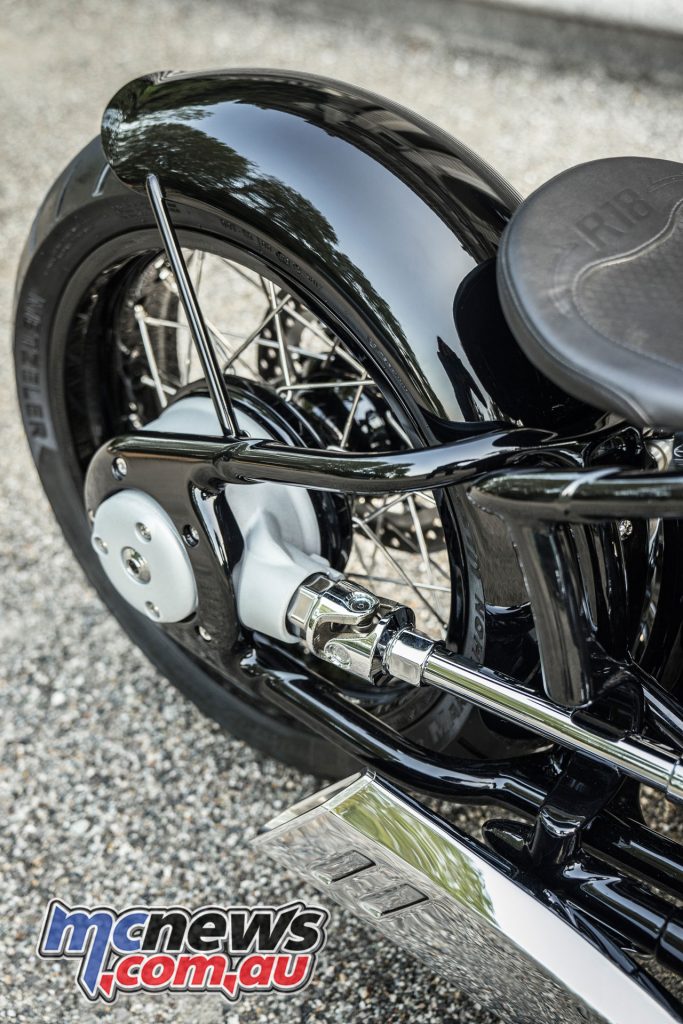
As in all BMW motorcycles with boxer engines, torque is transmitted from the gearbox to the rear wheel in the R 18 via a propeller-shaft or universal-shaft drive with universal joint, shaft and rear-axle drive with bevel and ring gear.
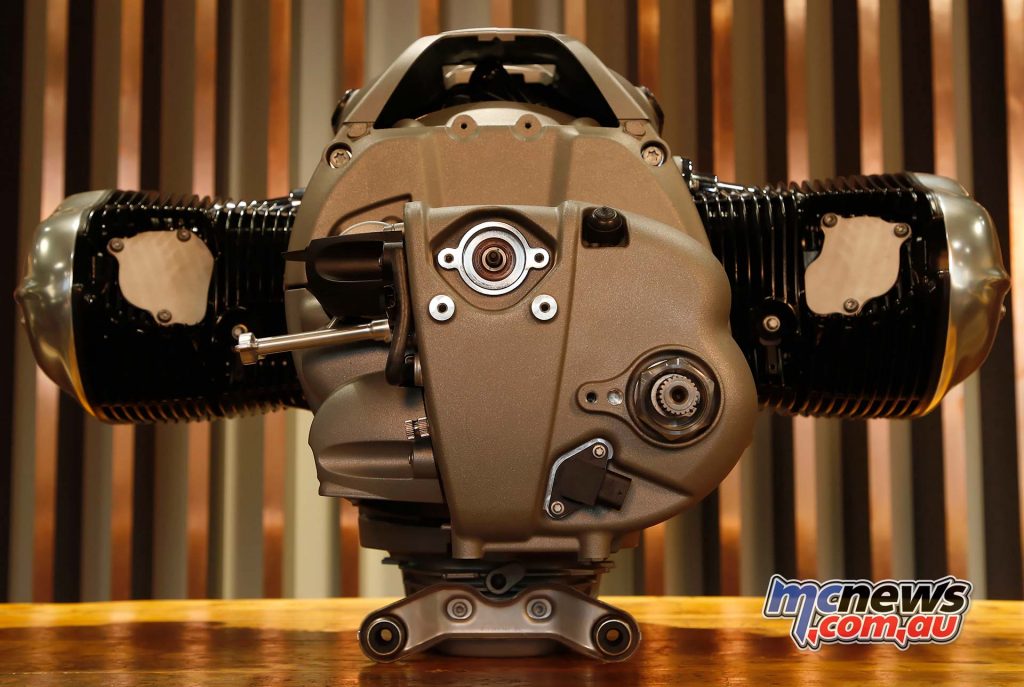

The propeller shaft and universal joint are examples of fascinating classic motorcycle technology since they are nickel-plated and open, as was commonly the case in BMW Motorrad models up to and including model year 1955. A so-called tripoid joint is applied on the gearbox side for the purpose of length compensation.






















