Honda Mobile Power Pack initiative
Honda have revealed further details around the Honda Mobile Power Pack or MPP, which will be the manufacturer’s portable and swappable battery system, and also seeks to address some of the issues inherent in some renewable energy with its implementation.
A big detail here was in achieving an adequate electricity supply-demand balance by installing a “buffer function” using MPP and other devices.
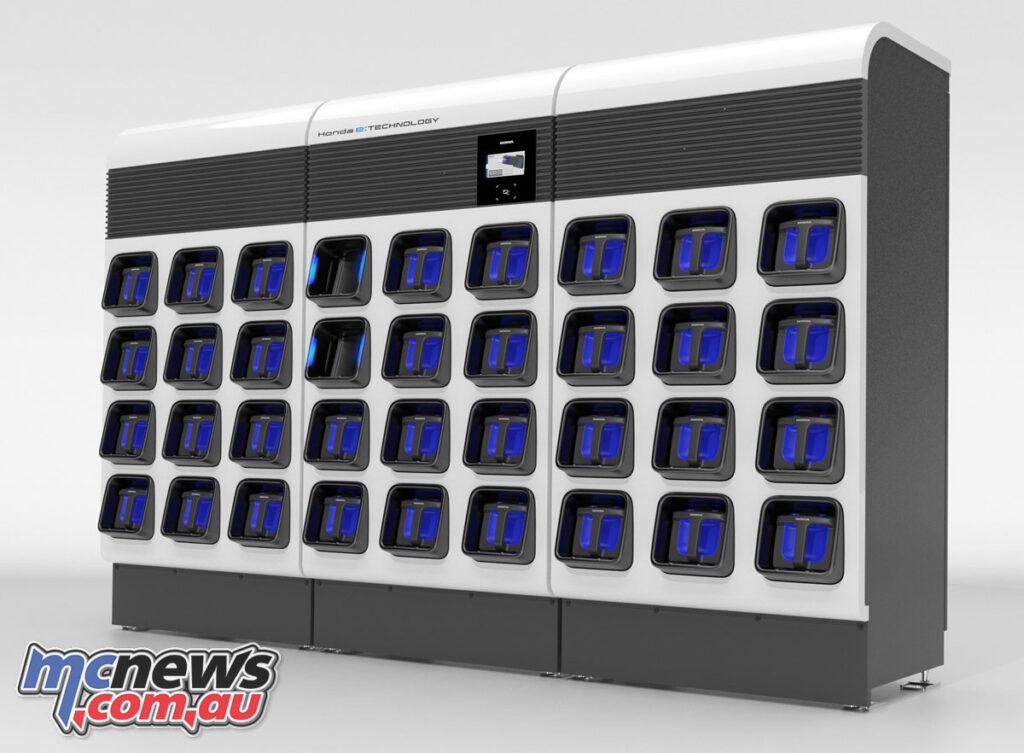

This is introduced as being to improve usability of renewable energy by addressing its sensitivity to natural conditions, by reducing the charging load on the power grid. Also considered is the possibility of supplying electricity stored in MPP back to the power grid in case of a power shortage. In other words, the batteries charge when renewable energy is available and feed back in when it’s not in a flexible way.
Honda is aiming for carbon neutrality for all products and corporate activities Honda is involved in by 2050, including developing the concept of “Honda eMaaS” through which Honda will contribute by connecting electrified mobility products and energy service.
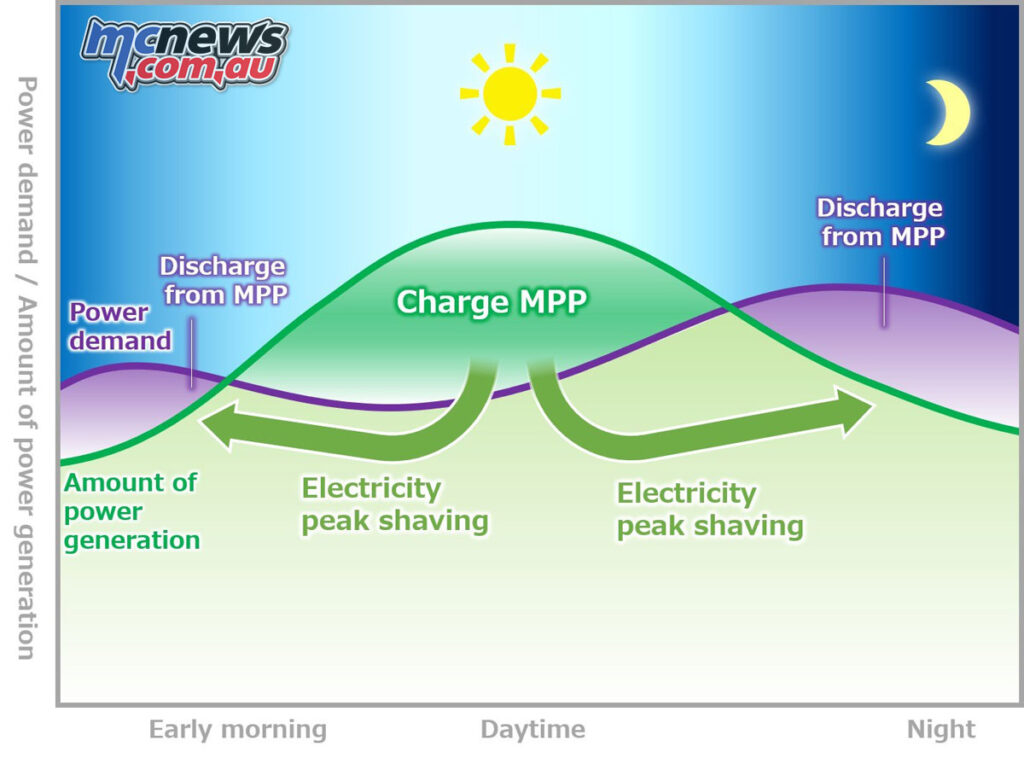
Based on this concept, Honda will expand the use of renewable energy by broadening the range of electrified products through electrification of its motorcycle and automobile products and through more utilisation of MPP and also by enabling infrastructure-linked smart power operations.
With the expanded use of MPP, it will become easier to use renewable energy which is sensitive to natural conditions. For instance, when an excess amount of electricity is generated during daytime hours through solar power generation, MPP will serve as a buffer by storing such excess electricity. Then, during late afternoon hours when electricity supply runs short of the demand, the electricity stored in the MPP during the daytime can be used to achieve peak-load shifting (or “peak shaving” that lowers and smooths out peak loads) to reduce the charging load on the power grid.

At the same time, Honda is also exploring secondary use (repurposing) of MPP when it becomes unsuitable for the use of mobility products due to a reduced battery capacity as a result of degradation, including uses as a storage battery for household use and as a power source for other products. To aid this Honda has been working toward the establishment of industry standards for portable and swappable batteries.
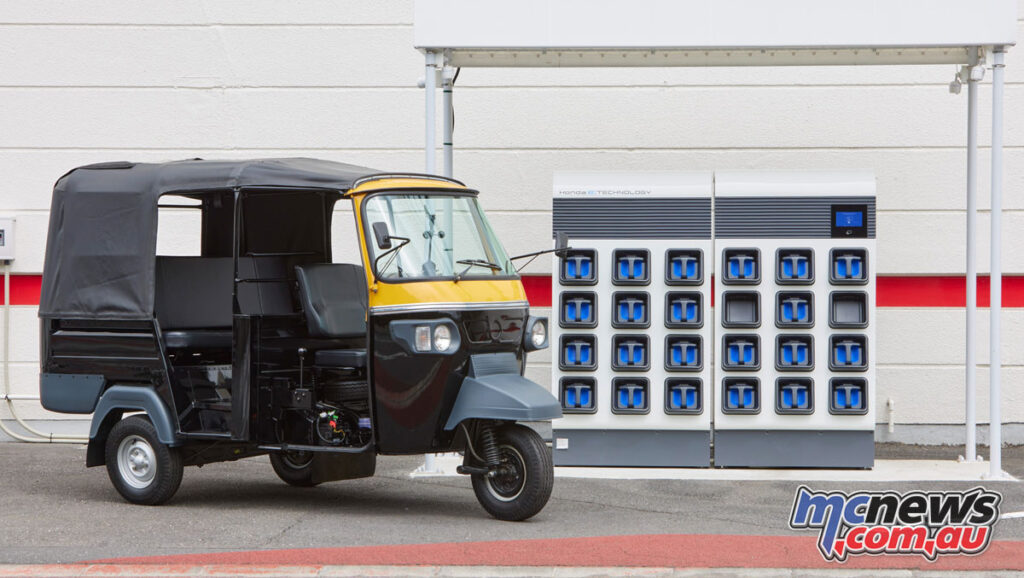
Honda introduced MPP in 2017. The utilisation of MPP began when it was applied to a Honda electric motorcycle model which went on sale in 2018. The new GYRO CANOPY e: business-use electric three-wheeled scooter which just went on sale features Honda Mobile Power Pack e: (MPP e:), an all-new MPP with an increased battery capacity.

Current projects focusing on MPP include:
- Since February 2019, Honda has been conducting demonstration testing in the Philippines for the utilization of surplus electricity using MPP and electric motorcycles for the purpose of realizing “local generation and local consumption” of electricity from renewable energy sources.
- Since July 2019, Honda has been conducting demonstration testing in Indonesia of battery sharing using MPP and electric motorcycles for the purpose of accelerating electrification of mobility products and expanding the use of renewable energy.
- Since February 2021, Honda has been conducting demonstration testing of battery sharing for electric tricycle taxies in India.
- In light of the results of this demonstration testing, Honda will begin a battery sharing service in India, using the MPP e: in the first half of 2022.

MPP e features
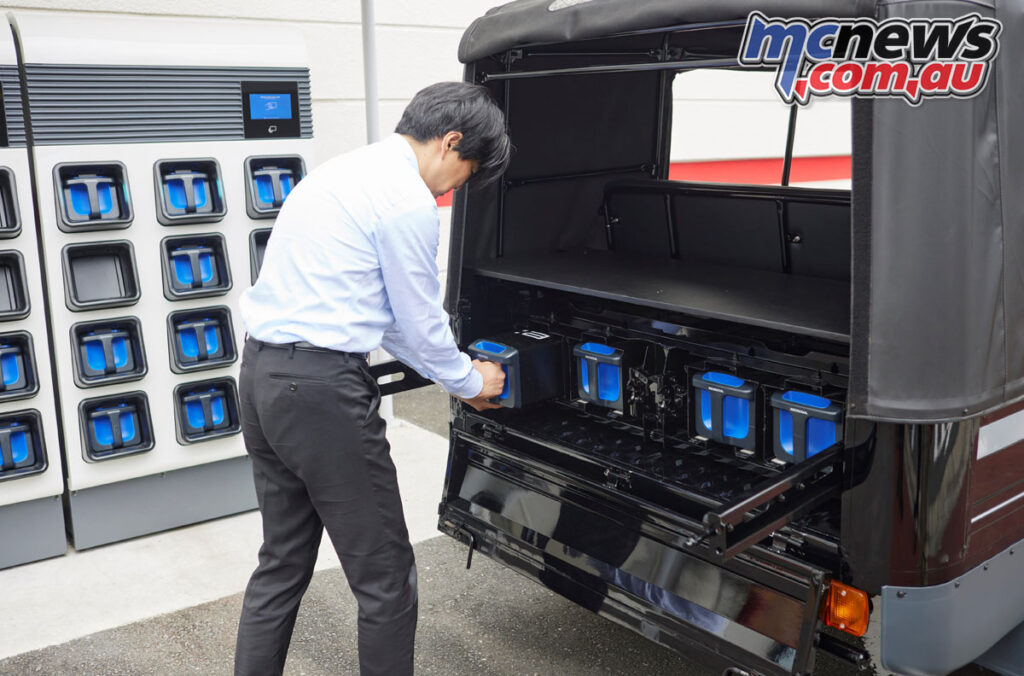
The MPP e is a lithium-ion battery capable of storing a large amount of electricity, more than 1.3kW, which can be utilized as a power source for a broad range of electric devices including small-sized mobility products.
- High versatility: In addition to mobility products, MPP e: can be utilized as a power source for a broad range of compatible devices.
- High durability: By considering heat dissipation during continuous discharging, deterioration due to high temperature is prevented, and sufficient water resistance, vibration resistance and shock resistance are ensured under the expected normal operating environment.
Data utilisation: The built-in control unit recognizes the conditions of the MPP e: and records the occurrence of all events. This data will be collected through the connector while MPP e is charging and then utilised for the battery sharing operation and other secondary uses.
























